Governor Lamont signs 22nd executive order to mitigate the spread of COVID-19
Governor Lamont today signed another executive order – the 22nd since he enacted the emergency declarations – that builds upon his efforts to encourage mitigation strategies that slow down transmission of the virus.
Governor Lamont’s Executive Order No. 7U enacts the following provisions:
- Protection from civil liability for actions or omissions in support of the state’s COVID-19 response: Protects health care professionals and health care facilities, including nursing homes and field hospitals, from lawsuits for acts or omissions undertaken in good faith in support of the state’s COVID-19 response. State statutes already provide similar protections for other first responders, including police, firefighters, and EMS.
- Financial protections for the uninsured and people covered by insurance who receive out-of-network health care services during the public health emergency: Protects those who are uninsured and those who are insured and are treated by an out-of-network emergency services health care provider from surprise bills and other significant costs. This will ensure that individuals receiving care are not being financially burdened.
Coronavirus Scams - Tips from Federal Trade Commission

Recordings of Scammy Calls About the Coronavirus:
Recordings courtesy of Nomorobo.
Additional information from Federal Trade Commission Consumer Information:
Undelivered goods: Online sellers claim they have in-demand products, like cleaning, household, and health and medical supplies. You place an order, but you never get your shipment. Anyone can set up shop online under almost any name — including scammers.
What to do: Check out the seller by searching online for the person or company’s name, phone number and email address, plus words like “review,” “complaint” or “scam.” If everything checks out, pay by credit card and keep a record of your transaction. If you’re concerned about the pricing of products in your area, contact your state consumer protection officials. For a complete list of state Attorneys General, visit naag.org.
Fake charities: When a major health event — like the Coronavirus — happens, you might be looking for ways to help. Scammers use the same events to take advantage of your generosity. Some scammers use names that sound a lot like the names of real charities. This is one reason it pays to do some research before giving. Money lost to bogus charities means less donations to help those in need.
What to do: Use these organizations to help you research charities. When you give, pay safely by credit card — never by gift card or wire transfer.
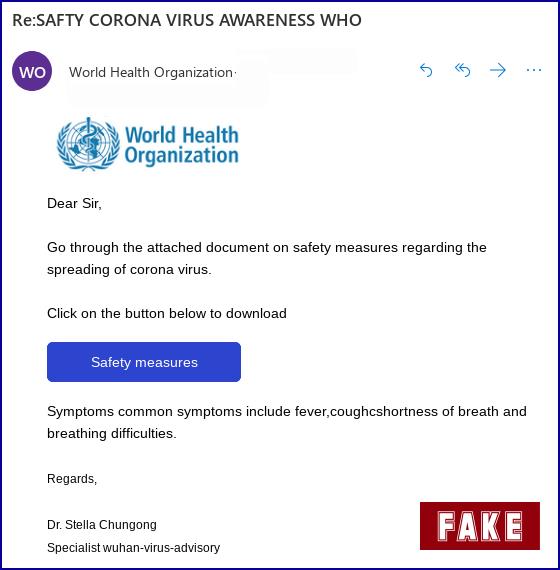
Fake emails, texts and phishing: Scammers use fake emails or texts to get you to share valuable personal information — like account numbers, Social Security numbers, or your login IDs and passwords. They use your information to steal your money, your identity, or both. They also use phishing emails to get access to your computer or network. If you click on a link, they can install ransomware or other programs that can lock you out of your data. Scammers often use familiar company names or pretend to be someone you know. Here’s a real-world example of a scam where phishers pretend to be the World Health Organization (WHO).
A fake email has the logo of the World Health Organization on it. (Sophos Ltd.):
Other scammers have used real information to infect computers with malware. For example, malicious websites used the real Johns Hopkins University interactive dashboard of Coronavirus infections and deaths to spread password-stealing malware.
What to do: Protect your computer by keeping your software up to date and by using security software, your cell phone by setting software to update automatically, your accounts by using multi-factor authentication, and your data by backing it up.
Robocalls: Scammers are using illegal robocalls to pitch everything from scam Coronavirus treatments to work-at-home schemes.
What to do: Hang up. Don’t press any numbers. The recording might say that pressing a number will let you speak to a live operator or remove you from their call list, but it might lead to more robocalls, instead.
Misinformation and rumors: Scammers, and sometimes well-meaning people, share information that hasn’t been verified.
What to do: Before you pass on any messages, and certainly before you pay someone or share your personal information, do some fact checking by contacting trusted sources. For information related to the Coronavirus, visit What the U.S. Government is Doing. There you’ll find links to federal, state and local government agencies.
To learn more, visit:
Want more information on the latest scams we’re seeing? Sign up for our consumer alerts. If you come across any scams or suspicious claims, report them to the FTC at ftc.gov/complaint.